CIRRUS Architecture
A look at the different components used to build CIRRUS and how they can be used to grow the reach of your science.
Basic CIRRUS Architecture
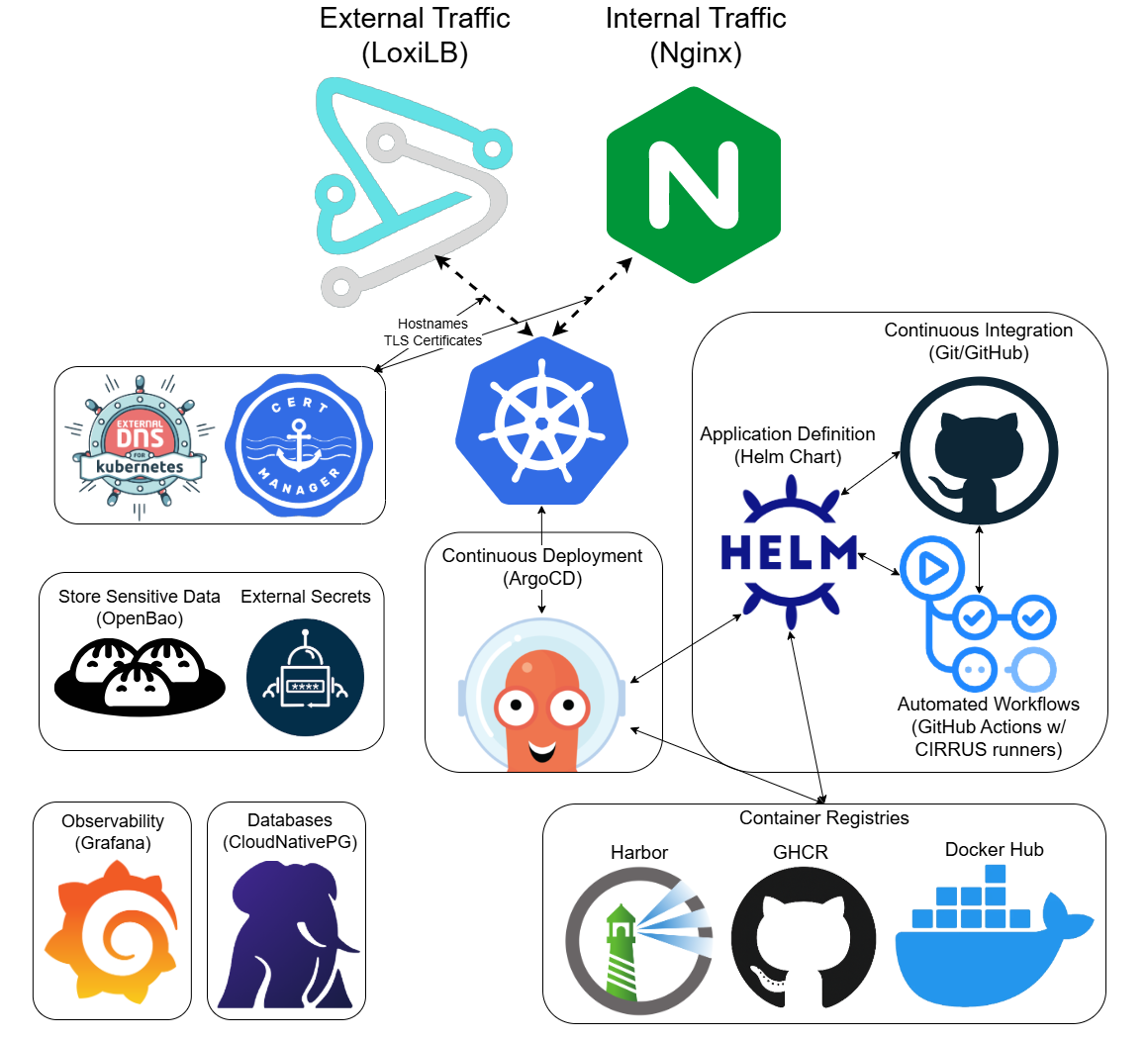
Understanding the CIRRUS Platform
CIRRUS is a cloud-native Kubernetes platform. This means applications designed to run on CIRRUS can run on any Kubernetes cluster—whether on-premises, in the cloud (AWS, GCP, Azure), or on other infrastructure. The platform uses industry-standard tools and practices, ensuring your work is portable and not locked into a specific environment.
What is a Container?
A container is a way to package your application with all the dependencies it needs to run, without including anything extra. It provides only what you need and makes reproducibility easy—your application runs the same way everywhere, whether on your laptop, a colleague's machine, or in production.
Starting with the Basics: Containers and Kubernetes
Kubernetes is a container orchestration platform that manages containerized applications at scale. Once you have a working container image, you store it in a container registry. CIRRUS provides Harbor as a private registry, and you can also use public registries like GHCR (GitHub Container Registry) or Docker Hub.
Defining Your Application: Helm Charts
Once your image is in a registry, it can be referenced in a Helm chart—a package that defines how your application deploys on Kubernetes, including configuration, resources, and dependencies.
Automation: CI/CD with GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions workflows automate your deployment pipeline. When you push code changes, workflows automatically build a new container image, push it to your container registry, update your Helm chart values to reference the new image, and trigger Argo CD to deploy the updated application.
With CIRRUS, you can connect a GitHub Actions Runner Scale Set to your repository. This provides access to more computational resources including GPUs, allowing your CI/CD workflows to run directly on the Kubernetes cluster with the hardware your builds and tests require.
Continuous Deployment: Argo CD
Argo CD continuously monitors your Helm charts in Git repositories. When changes are detected, it automatically syncs and deploys your application to the Kubernetes cluster, implementing true GitOps practices.
Accessing Your Application: Ingress and TLS
CIRRUS provides two ingress paths: LoxiLB for external traffic using BGP peering to provide publicly accessible endpoints, and NGINX Ingress for internal traffic within the UCAR network.
ExternalDNS automatically creates DNS records in the *.k8s.ucar.edu domain for your services, while cert-manager issues and manages TLS certificates from Let's Encrypt to provide HTTPS endpoints for your web applications.
Security: Secrets Management
OpenBao works with the External Secrets Operator to securely store sensitive data like API keys, passwords, and credentials. Secrets are encrypted at rest in OpenBao and securely injected into your containers with encryption in transit, ensuring sensitive information never lives in your Git repository or Helm charts.
Databases: CloudNativePG
If your application needs a database, CIRRUS offers CloudNativePG—a Kubernetes operator that deploys and manages highly available PostgreSQL clusters with automated backups, failover, and scaling.
Observability: Monitoring and Logging
CIRRUS provides access to Grafana, which integrates with Prometheus (for metrics) and Loki (for logs) to gather telemetry from your applications. You can create custom dashboards to analyze and monitor application performance, set up alerts, and troubleshoot issues.
